Total Pageviews
Sunday 28 August 2016
Sunday 21 August 2016
Saturday 20 August 2016
There is and there are
Remember
Have = possession (personal)
I have a dog.
I have 2 dogs.
There is/are = existence
There is a dog in the park.
There are 2 dogs in the park.
YOU CAN NOT SAY
HAVE 2 DOGS IN THE PARK.
Sunday 14 August 2016
Wednesday 10 August 2016
Verbs in the past.
Simple past tense: regular and irregular verbs from monica_llovet
LIST ONE
LIST TWO
LIST ONE
Infinitive
|
Verb in the Simple
|
To be
|
Was/were
|
Begin
|
Began
|
Blow
|
Blew
|
Break
|
Broke
|
Bring
|
Brought
|
Buy
|
Bought
|
Catch
|
Caught
|
Choose
|
Chose
|
Come
|
Came
|
Do
|
Did
|
Draw
|
Drew
|
Drink
|
Drank
|
Drive
|
Drove
|
Eat
|
Ate
|
Fall
|
Fell
|
Feel
|
Felt
|
Fight
|
Fought
|
Find
|
Found
|
Get
|
Got
|
Give
|
Gave
|
Have
|
Had
|
Infinitive
|
Verb in the Past
|
Grow
|
Grew
|
Keep
|
Kept
|
Know
|
Knew
|
Leave
|
Left
|
Lose
|
Lost
|
Make
|
Made
|
Put
|
Put
|
Read
|
Read
|
Run
|
Ran
|
Say
|
Said
|
See
|
Saw
|
Send
|
Sent
|
Sit
|
Sat
|
Speak
|
Spoke
|
Take
|
Took
|
Teach
|
Taught
|
Think
|
Thought
|
Throw
|
Threw
|
Wake
|
Woke
|
Win
|
Won
|
Write
|
Wrote
|
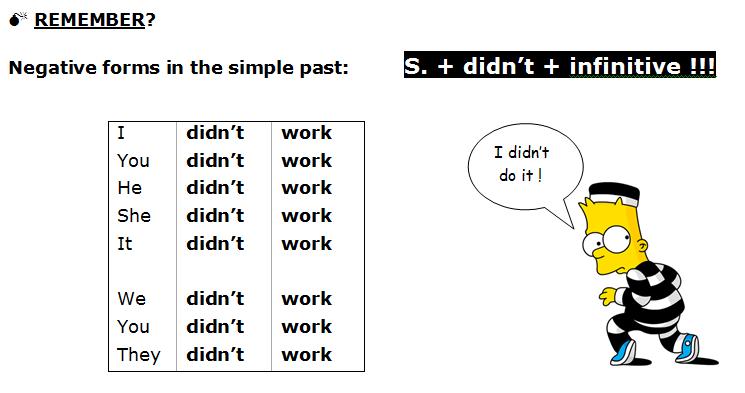
REMEMBER: FOR THE NEGATIVE OR QUESTION FORMS
DIDN'T + VERB (INFINITIVE)
He didn't see the monster.
She didn't read the book.
They didn't do their homework.
DID + SUBJECT + VERB (INFINITIVE)?
Did you play football yesterday?
Who did you play with?
Why did you leave early?
Where did they play?
Focus on Tall Tales : “Paul Bunyan, the Mightiest Logger of Them All”
Reading Comprehension Questions
After reading the Tall Tale; “Paul Bunyan, the Mightiest Logger of Them All”,(page 110) circle the answer that correctly answers each comprehension question.
1.Paul was so big that his parents ....
a. made him live in a cave far from civilization.
b. rode on his shoulders everywhere he went.
c. slept in his beard on cold nights.
d. fed him with a spoon made from a tree trunk.
2.Paul created the Grand Canyon by ...
a. dragging his pickaxe behind him.
b. tripping over the rocky Mountains.
c. lying down for a nap.
d. writing his name in the sand.
3.What was one requirement of Paul Bunyan’s loggers?
a. They had to be over ten feet tall.
b. They had to be sider that white pine logs.
c. Their hands had to be two feet wide.
d. They had to swing an axe in the blink of an eye.
4.The Great Lakes were formed when Paul ...
a. scooped through the dirt to find worms for fishing.
b. left footprints in the mud when walking from Maine to Minnesota.
c. dug a few ponds for his loggers to drink from.
d. mined for gold so he could buy clothes for the crew.
5.During the year of the Hard Winter, it was so cold that ...
a. snowmen went south for the winter.
b. words froze in the air.
c. loggers froze in their bunkbeds.
d. Paul’s whiskers broke off like icicles.
6. In your own words, describe the features of a tall tale.
Reading is Fundamental
Houghton Mifflin Reading - 5th Grade - Expeditions - Focus on Tall Tales
http://www.davis.k12.ut.us/cms/lib07/UT01001306/Centricity/Domain/1621/Reading%20Study%20Guides/Focus%20on%20Tall%20Tales/Focus%20on%20Tall%20Tales.pdf
Monday 8 August 2016
Tuesday 2 August 2016
Point of View & Narrator's Perspective Lesson | Teaching Common Core Rea...
The Narrator
or WHO ARE YOU? AND WHY ARE YOU TELLING ME THIS?
A crucial element of any work of fiction is the NARRATOR, the person who is telling the story (note that this isn't the same as the AUTHOR, the person who actually wrote the story).
What types of narrators are there? The first major distinction critics make about narrators is by person:
a FIRST PERSON narrator is an "I" (occasionally a "we") who speaks from her/his subject position. That narrator is usually a character in the story, who interacts with other characters; we see those interactions through the narrator's eyes, and we can't know anything the narrator doesn't know.
a SECOND PERSON narrator speaks in "you." This is an extremely rare case in American literature, although we will read a few examples.
a THIRD PERSON narrator is not a figure in the story, but an "observer" who is outside the action being described. A third-person narrator might be omniscient (ie, able to tell what all the characters are thinking), but that is not always the case. Third-person narration may also be focalized through a particular character, meaning that the narrator tells us how that character sees the world, but can't, or at least doesn't, read the mind of all the characters this way.
http://academic.reed.edu/english/courses/analyzinglit/narrator.html
https://www.brainpop.com/english/writing/pointofview/
1. What is point of view?
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)